Zhang Feng published the second type of CRISPR-Cas system introduction
Recently, Professor Zhang Feng and two other scholars published a close-up article entitled "SnapShot: Class 2 CRISPR-Cas Systems" in Cell magazine, introducing a new generation of CRISPR genome editing system: Class 2 CRISPR-Cas Systems.
In 2015, Zhang Feng and his colleagues reported that they discovered a different CRISPR system with the potential to achieve simpler and more accurate genome engineering operations. The new system searches for hundreds of species of CRISPR systems in different types of bacteria to find enzymes with useful properties, resulting in new Cpf1 enzymes from the genus Acidaminococcus and Lachnospiraceae. Candidates.

This newly discovered Cpf1 system has several important aspects that differ from the previously described Cas9, which was mentioned in the article by Zhang Feng Cell, the first-generation CRISPR genome editing system, which is the first of its kind: the Cpf1 system is simpler. It only needs one RNA. The Cpf1 enzyme is also smaller than the standard SpCas9, making it easier to transfer into cells and tissues; Cpf1 cleaves DNA in a different way than Cas9. When the Cas9 complex cleaves DNA, it cleaves two strands of the same locus, leaving the "blunt ends" often mutated when reconnected. The two strand cuts created with the Cpf1 complex are offset, leaving a short overhang at the bare end. This is expected to facilitate precise insertion, allowing researchers to integrate a piece of DNA more efficiently and accurately; the Cpf1 nick is far from the recognition site, which means that even if the target gene is mutated at the cleavage site, it can be re-cut, provided multiple times. Opportunity to correct editing; the Cpf1 system provides new flexibility for selecting target sites. Like Cas9, the Cpf1 complex must be preferentially attached to PAM, a short sequence, and the selected target is close to the naturally occurring PAM sequence. The PAM sequence recognized by the Cpf1 system is quite different from Cas9. This may be an advantage when targeting certain genomes such as Plasmodium and the human genome.
This latest review provides a more general description of the system, as shown in the following figure:
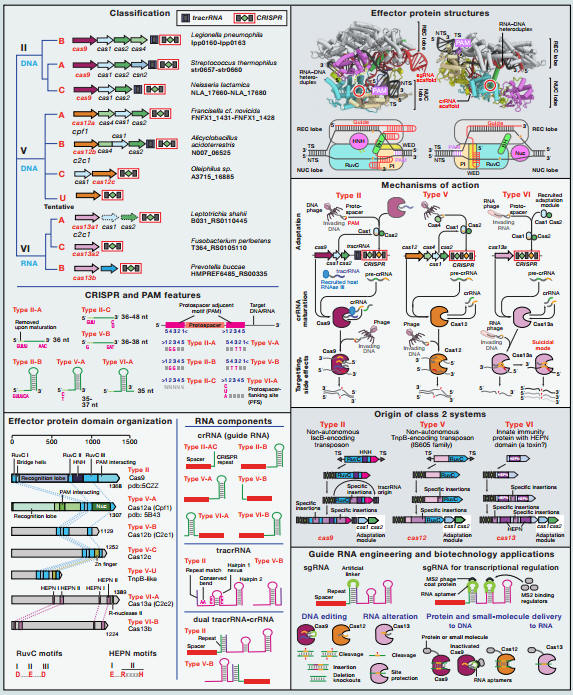
The article points out that the second type of CRISPR-Cas system is based on different family of effector proteins and can be divided into three types and nine subtypes, of which Cas9 and Cas12a (Cpf1) have been successfully used in genome engineering. In previous studies, Zhang Feng's team also used a new bioinformatics method to discover new proteins temporarily named C2c1, C2c2, and C2c3. They developed a series of computational methods to search the NIH genome database for identification. The new CRISPR-Cas system (see: Cell: The second generation of genetic editing artifacts is born, CRISPR/Cpf1 makes everything possible!).
Finished Pharmaceutical Products
The definition of Finished Pharmaceutical Product can be found in § 4 (1) of the Medicines Law. It reads: "Finished drugs are drugs that are prepared in advance and sold in specific packaging to the consumer..." The drugs are mostly in the form of tablets, capsules, drops, liquids, ointments and suppositories. For Phytotherapy (healing with plants) numerous drugs are also available in pharmacies in which drugs or drug preparations are processed. One distinguishes between the drug preparations: the chopped drug to prepare a tea, the milled drug (= drug powder) and the dried extract for the manufacture of tablets, capsules and pills, tincture for the preparation of drops and the fluid extract for juices, salves and other ointments to name a few. A finished drug with a drug formulation is called an "herbal medicine" or phytopharmacon (plural: phytopharmaceuticals).
Finished Pharmaceutical Products,Otc Pharmaceutical Products
NOUVASANT GROUP LTD. , https://www.nouvasant.com
