William R. Rassman, the father of global hair transplant, and FUT and FUE, two internationally recognized hair transplant technologies
The development of the hair transplant industry is inseparable from the promotion of technology, and excellent doctor experts play an important role in it.
William R. Dr. Rassman is a well-known hair transplanting expert in the international hair transplanting industry and is known as the “father of global hair transplantâ€. He and another hair transplant expert Robert M. Dr. Bernstein invented the most popular FUE and FUT hair transplantation technologies in the world. These two technologies have epoch-making significance in the history of hair transplantation, and the arterial network has arranged this.
Dr. Rassman received his MD from the Virginia Medical School in 1966. He then underwent a surgical internship at the University of Minnesota, and served as a general surgery resident at the Cornell Medical Center and Dartmouth Medical Center, and was certified by the American College of Surgeons in 1976.
In 1991, Dr. Rassman founded the New Hair Institute (NHI), where he began his research on hair transplantation and quickly became a global leader in hair transplantation technology.
With continuous technological innovation and equipment inventions, Dr. Rassman has set a record for the number of hair transplants in a single operation. In 1994, he became the first doctor in the world to complete a single transplant unit of 2000, 3000 and 4000. Other doctors have only had hundreds of hair transplants.
In 2004, the World Hair Development Association awarded the “Golden Hairbag Award†for its outstanding achievements in hair transplant technology.

William R. Dr. Rassman
Demystifying two hair transplant technologies: FUT and FUE
In 1995, Dr. Rassman and Dr. Bernstein jointly created a new generation of hair transplant technology, FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation), with FU (Follicular Unit) as the basic unit for hair follicle separation and planting.
The main process of FUT technology:
1. After local anesthesia of the scalp, surgically remove the skin and subcutaneous tissue containing the hair follicle from the donor area of ​​the scalp (generally selecting the posterior occipital region), that is, a 6 to 10 inch flap in the form of a thin strip;
2. Separate the hair follicles that need to be transplanted under a microscope. The specific step is to divide the peeled scalp into 500 to 2000 small pieces, each of which has a hair or a few hairs;
3. After nuclear energy nutrition, the extracted hair follicles are transplanted to the bald area on the scalp of the patient. These two processes—extracting the hair follicles and suturing the flaps and transplanting—caused small surgical wounds. The scalp that is "stripped" from the donor may leave a scar after the wound has healed.
Compared to previous technologies, FUT technology has the following significant advantages:
1. The hair follicles are separated and planted according to the natural condition of the follicular unit, and each follicular unit contains only 1-4 hairs;
2, using a microscope to separate hair follicles, can reduce hair follicle damage by 30-50% compared with the traditional naked eye, saving patients precious hair follicle resources;
3. Using this technology, the survival rate of hair follicle transplantation is as high as 95%, which is much higher than the survival rate of traditional hair transplantation technology. The maximum transplant volume in a single operation is as high as 3000-4000 follicular units, and the hair density in the transplanted area is higher, and the transplant effect is more natural.
In 2001, Dr. Rassman proposed a new hair-planting technique, FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction), which can extract follicular units (FU) directly from the patient donor area, rather than cutting a flap first and performing it before transplantation. Separation. This technique can reduce hair follicle infestation and avoid leaving scars in the donor area after surgery. With the maturity of this technology, hair transplant surgery is gradually becoming a "minimally invasive surgery" that does not require surgery.
The main process of FUE technology:
1. According to the patient's medical history, scalp characteristics and hair loss, and the effect that the patient hopes to achieve by hair transplant, the attending physician will measure the hair density of the donor area of ​​the posterior occipital region and determine the number of hair follicles transplanted by each patient through FUE technology;
2, the surgical process will use a special precision instrument: use a biopsy needle to cut a small mouth around the transplanted hair follicle, and then use a small surgical forceps to extract a single hair follicle from the donor area, and sometimes need to use a special needle to the hair follicle fiber Separated from the subcutaneous tissue. After the scalp is taken, it will heal automatically without stitching. In addition, hair follicles can be extracted from multiple regions rather than a single site, so the hair thickness of the donor region is not affected;
3. The removed hair follicles are placed in the culture solution for cultivation to improve the survival rate. The monomer implantation is then carried out according to the normal hair growth density.
Dr. Rassman said, “FUE is suitable for people who need to transplant a small amount of hair for a long time, people who have to shave their heads for professional reasons (such as models), people who have a bad history or have scars, and people who can improve the scalp scar by hair transplantation. Wait."
“But not all hair loss patients are suitable for FUE techniques, such as patients with large-area hair loss. Because the number of hair follicles extracted each time during a hair transplant is limited, too much extraction will result in unnatural hair in the donor area. â€
“FUE is technically demanding. Anyone who lacks proper training should not perform this procedure. Appropriate training includes an assessment of the patient to determine the suitability of the FUE technique. For example, biopsy the donor area to Determine the characteristics of the hair follicle and the ease of extraction."
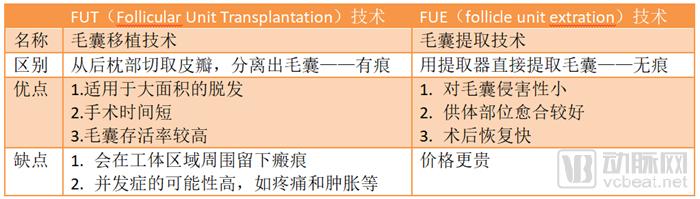
Comparison of two major technologies
Risk of hair transplant surgery, postoperative care and costs
As with any surgery, hair transplants have a certain risk, and some adverse reactions are common in hair transplant patients. Such as major bleeding, infection, swelling of the scalp and face, scarring, thinning of the hair and itching, growing unnatural patchy new hair.
Facial swelling is common and may last for a few days after surgery. Swelling usually starts from the scalp and gradually transitions to the forehead and face. The swelling will dissipate in a week or so. When new hair begins to grow, some people will develop folliculitis, and antibiotics can alleviate this symptom.
It is also possible for the patient to find the shedding of the original hair where the new hair grows, a condition known as "shock loss." But this is usually not permanent and the hair will grow again over time.
In order to prevent infection, resolve discomfort, and ensure the best results, postoperative care for hair transplants is very demanding, such as raising the head during sleep, avoiding strenuous exercise, using cold compresses to reduce swelling, and taking regular medications for insomnia and pain. .
The scalp may become very sensitive after surgery, and the patient needs to wear a bandage on the scalp for at least one to two days. Drugs that need to be taken after surgery, such as hypnotics, painkillers, antibiotics to prevent infection, anti-inflammatory drugs for stopping bleeding, cortisone, minoxidil, and drugs for treating hiccups and itching often have some side effects.
The time to recovery depends on the type of hair transplant and the area of ​​hair transplant, and patients who use FUE technology recover faster. Most people can get back to work 2 to 5 days after surgery. If sutures are used, they will be removed within 10 days. Within 2-3 weeks after surgery, the transplanted hair may begin to fall off, which is normal in the first few months. Most people will see 60% of new growth after 6-9 months.
These adverse reactions, as well as the need for continued postoperative care, can cause alopecia patients to develop aversion or rejection of hair growth. High surgical costs are a major factor limiting the global hair transplant market and a current disadvantage in this area.
This minimally invasive procedure has been popular in the United States since the 1950s. Although it is the most effective method for treating hair loss, it is an expensive procedure from a treatment and recovery perspective.
The cost of hair transplant varies widely and varies from one factor to another, but typically ranges from $4,000 to $15,000. Factors affecting cost include: the number of hair transplanted, the choice of hair transplant technology, the length of surgery, and the choice of the attending physician.
In addition, it should be noted that most insurance companies regard hair transplants as a cosmetic surgery, so many insurance plans do not include hair transplant surgery. However, some hospitals or clinics offer payment options, and patients with hair loss can pay for surgery in installments. In addition to the cost of performing a hair transplant, it may involve the cost of recovery, such as the expenditure of follow-up drugs such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers.
For some people, hair transplant costs are too high, and non-surgical methods can replace hair transplant surgery to treat hair loss. The American Academy of Dermatology lists some of the most common alternatives to implant surgery:
1. Minoxidil (collapsed): over-the-counter drugs that can be used by both men and women;
2, finasteride (protection method): for male patients only, this medicine can promote hair regeneration or relieve hair loss;
3, estrogen: women who experience hair loss can take estrogen drugs;
4, cortisone: local and injectable cortisone can accelerate the hair growth of some patients;
5, laser treatment: low-dose laser treatment can be used to treat hereditary alopecia and alopecia areata.
Trends in the hair transplant market and the application of emerging technologies
According to a survey released by the International Society for the Development of Hair (ISHRS) in September 2017, the hair transplant market is at a critical juncture. In 2016, 635,189 implants were performed worldwide, including 195,284 in Asia, 149,400 in the Middle East, and 133,136 in the United States. Overall, from 2014 to 2016, the number of implants worldwide increased by 60%.
In 2016, there were 597,181 surgical patients (67% more than in 2014) and 1,241,764 non-surgical patients (an increase of 78%).
It is estimated that the global hair transplant market has grown from $2.5 billion in 2014 to $4.1 billion in 2016. This means that the market size has increased by 64% compared to 2014. The CAGR (composite annual growth rate) of the global hair care service market is expected to reach around 20% in 2018-2023.
Other notable trends and facts in the ISHRS survey include:
1. In 2016, more than half of male and female surgical patients worldwide were between 30 and 49 years old, with 59.7% and 59.0% respectively;
2. The proportion of men who received surgery (85.7%) was higher than that of women (14.3%);
3. The number of hair transplant operations in the Middle East increased the most, up 163% from 2014.
It is expected that the CAGR in the Asia Pacific region will be the highest. Celebrity effects, media influence, awareness growth, attention to their appearance, pressure from peers, pressure from society, urbanization, high incomes and growing word of mouth are potential drivers of the hair transplant market in the Asia Pacific region. Currently, North America has the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific.
For the development of Chinese hair transplant technology, the father of global hair transplant, William R. Dr. Rassman pointed out that China's hair-planting technology has been in development since 2007 and has been in existence for 11 years. However, China's development in this field is very rapid, and now it can be level with the US technology in terms of quality, so it is very optimistic about the Chinese market.
In the past six years, Dr. Rassman and his team have combined FUT technology with SMP (Scalp MicroPigmentation) in practice, trying to break through the limitations of the prior art. SMP is a minimally invasive cosmetic technique in which micro-pigment is pigmented on the dermis of the scalp. By patterning a highly dense dot pattern on the scalp, the color and appearance of the scalp can be changed to make the patient's hair look thicker.
Dr. Rassman said, "In most traditional hair transplants, if you continue to lose hair or want thicker hair, you may need a second or even three operations to achieve the desired results. And FUT technology is not suitable for large areas or Dispersion-type hair loss. When SMP technology is used instead of the second hair transplant operation, the number of hair transplant operations can be reduced, the cost of treating hair loss can be reduced, and the expected therapeutic effect can be achieved."
“For large or diffuse hair loss, there is currently no effective medical or surgical treatment (including hair transplant). For medical institutions, learning SMP technology has the opportunity to open up this market with great potential, because SMP is relative to hair transplant technology. It's easier to learn. Doctors can use this to expand the range of services and provide better non-surgical treatment for patients with hair loss."
With the popularity of FUE and SMP, doctors can now solve most of the hair loss problems, and this technology is likely to become a standardized product and process for the treatment of hair loss.
Frozen Pud Red Shrimp,Red Shrimp,Frozen Shrimp,Melantho Shrimp
Zhoushan Haiwang Seafood Co., Ltd. , https://www.haiwangseafoods.com
