Common pests and diseases of cruciferous vegetables and biological control techniques
China is a big country in the production and consumption of vegetables, and people's growing demand also indicates the need for healthier and more environmentally friendly vegetables. What are the common pests and diseases of cruciferous vegetables? Today, Huinong.com will explain the main pests and diseases of cruciferous vegetables and their biological control techniques.

1 The main pests and diseases of cruciferous vegetables and their occurrence conditions
1.1 Main disease types and occurrence conditions of cruciferous vegetables
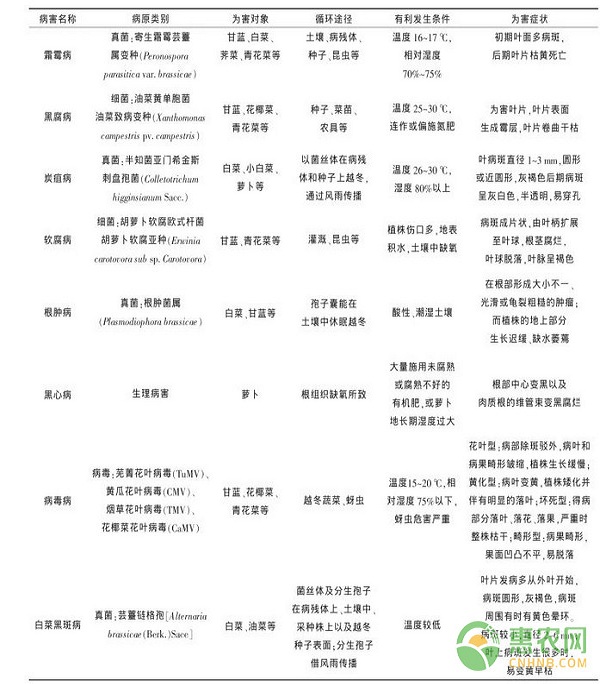
The main diseases of cruciferous vegetables include downy mildew, black rot, anthracnose, soft rot, viral disease, black spot, radish black heart disease, etc. The conditions and symptoms are shown in Table 1.
1.2 Main pest species and occurrence conditions of cruciferous vegetables
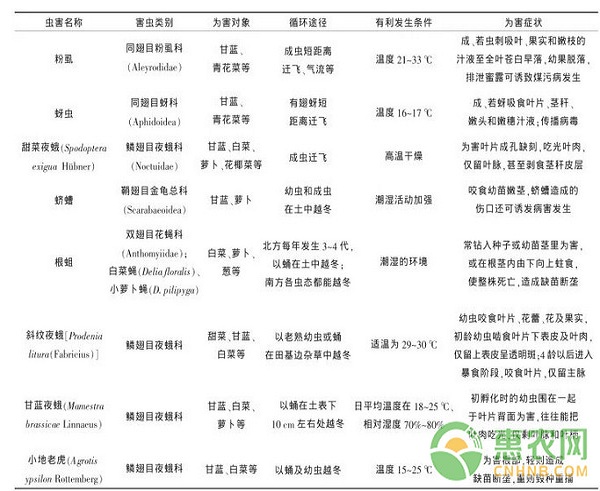
The main pests of cruciferous vegetables include cabbage caterpillar (P. rapae larvae), Plutella xylostella, whitefly, white locust, beet armyworm, cockroach, root cockroach (whitefly, radish fly), Spodoptera litura, cabbage moth, and small tiger , yellow curved strips, radish borers (cabbage larvae), locusts and so on. The conditions for the occurrence of major pests and the symptoms of the damage are shown in Table 2.
Table 1 Main diseases of cruciferous vegetables and their occurrence conditions
2 Biocontrol technology for main pests and diseases of cruciferous vegetables
2.1 Main disease biological control technology
2.1.1 When downy mildew disease is found in the center of the diseased plant or the disease center, timely spraying and controlling the disease. The medicament may be selected by using a 5% amino oligosaccharide aqueous 500-fold dilution and a 150 million cfu/g Trichoderma WP 400-fold dilution, and mixing and applying. When spraying, the main back of the sprayed leaf is dominated by the central diseased plant. Apply once every 7 days, even spray 2 or 3 times; or use Bacillus licheniformis water to control, apply 100 billion / mL of Bacillus licheniformis 150-300 times diluted solution per 667m2, apply every 7d 1 Then, spray 2 to 3 times; or spray with a 27% high-fat membrane water emulsion 200 times dilution.
2.1.2 In the early stage of radish black rot, 72% agricultural streptomycin sulfate or 90% neomycin-containing 4 000-fold dilution solution was used to irrigate the roots, and the roots were irrigated every 7-10 days for 3 times.
2.1.3 In the early stage of anthrax disease, spray disinfection with 2% Wuyimycin water 150~200 times dilution; or spray with 2% agricultural anti-120 water 150 times dilution, spray once every 7~10d , continuous medication 3 times.
2.1.4 Soft rot found that the diseased plant was immediately pulled out and removed from the field for treatment. The diseased cavity was sprinkled with 72% agricultural streptomycin sulfate or 90% neomycin or lime. In the early stage of the disease, spray treatment was carried out with a 500-fold cfu/g Bacillus polymyxa WP 500-fold dilution, sprayed once every 7 days, and sprayed 2 to 3 times. In the seedling stage and the rosette stage, the mixture was sprayed once with a 3% carbendazim WP 500-fold dilution.
Table 2 Main pests of cruciferous vegetables and their occurrence conditions
2.1.5 The virus disease begins to control the vegetable meal. See the prevention and control of mites. Before the disease occurs, spray with 8% Ningnanmycin water or 0.5% amino oligosaccharide 500 times diluted solution, spray once every 7 to 10 days, continuously for 3 times; or use 10% mixed fatty acid. The water emulsion (83 antagonist) is sprayed with a 100-fold dilution before or after the seedling, which can effectively prevent viral diseases.
2.1.6 In the early stage of black spot disease, spray with 2% agricultural anti-120 water agent 150-200 times diluted solution; or spray with 2% Wuyimycin water 100 times diluted solution, spray every 6-8 days Second, a total of 2 to 3 times.
2.1.7 Sterilization of radish black heart disease seeds: 20kg seeds were immersed in 15mL of 3% carbendazim (Nongkang 751) wettable powder 100 times diluted solution, and then sown after being absorbed. After emergence, 72% agricultural streptomycin-soluble powder 3 500-fold dilution or 3% carbendazim (agricultural anti-751) wettable powder 500-fold dilution or 90% neomycin-based wettable powder can be diluted 3 000 times. The liquid is sprayed and controlled, sprayed once every 10 days, and sprayed a total of 2 to 3 times.
2.2 Main pest biological control technology
2.2.1 The cabbage caterpillar releases the parasitic eggs of the Trichogramma to control the cabbage caterpillar. Trichogramma parasitizes eggs, puts bees at the spawning stage of pests, puts 10,000 bees per acre, puts bees once every 5-7 days, and continuously puts bees 3 to 4 times; or uses Bacillus thuringiensis ( Bt preparation) or rapeseed · Suyun bacteria control of cabbage caterpillar, in the egg hatching period, every 667m2 with 32000IU / mg Bt wettable powder 1200 ~ 1500 times dilution or 16 000 IU / mg Bt suspension agent 600 ~ 750 times diluted The liquid is sprayed and controlled, and the application is better in the evening, and then sprayed once after 10 days; or the plant source preparation 0.3% azadirachtin is used to control the cabbage caterpillar. Before the larval hatching period to 2 years before the larvae, the 650-900 times dilution of 0.3% azadirachtin emulsifier was sprayed and controlled every 667 m2, and sprayed once every 7-10 days, and sprayed twice continuously.
2.2.2 Plutella xylostella is controlled by Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt preparation) or Plutella xylostella granulosis virus. Before the age of egg hatching until the age of 2 years of larvae, use 32000 IU/mg Bt wettable powder 900-1200 times dilution or 16000 IU/mg Bt suspension agent 450-600 times dilution per 667 m2, or use Plutella xylostella granule virus every 667 m2. 30 billion OB / mL suspension agent 25 ~ 30 mL for spray control, evenly spray the front and back of the leaves, spray in the evening is good, spray again after 10d; or use plant source preparation 0.3% azadirachtin EC to control Plutella xylostella . Before the egg hatching period until the larvae 2 years old, the front and back sides of the leaves were uniformly sprayed with a dilution of 0.3-100% azadirachtin emulsifiable concentrate, and sprayed once every 7-10 days, and sprayed twice continuously.
2.2.3 The whitefly is used to control the greenhouse whitefly. The bee is parasitic in the nymphs and mites of the whitefly, after the parasitic, the pests are black and dead, and the nymphal parasitic rate is more than 75%; or the predatory natural enemies, the black ladybug, are released to control the whitefly. The greenhouse crop release is 1 adult / 1.39 ~ 9.29 m2.
2.2.4 Aphids use a bee sting to control aphids. When the locusts first saw the locusts, 12 dead cockroaches were released per square meter, and every 7 days, a total of 7 times were released; or the pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae was used to control aphids, using 10 billion spores/g of Metarhizium 500 Spray ~800 times the dilution solution, spray once every 7 days for 2 to 3 times.
2.2.5 Beet armyworm release of Trichogramma spp. to control beet armyworm; or use Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt preparation) to control beet armyworm, 32000 IU/mg Bt wettable powder 750 during egg hatching to 2nd instar larval stage ~1 200 times dilution for spray control, better application in the evening; or control of beet armyworm with nuclear polyhedrosis virus, sprayed with 300 million PIB / g beet armyworm nuclear polyhedrosis virus 300 ~ 400 times dilution Control, every 10d1 times, continuous spraying 1~2 times; or use plant-derived pesticide azadirachtin to control beet armyworm, use 0.3% azadirachtin emulsion to dilute 400-600 times for spray control, every 7d, continuous spraying 1 or 2 times.
2.2.6 蛴螬 白 白 白 白 白 和 和 和 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白 白3 times.

2.2.7 Root cockroach (Baicus flave, radish fly) Do not use unfertilized fertilizer, even if using fully decomposed organic fertilizer, pay attention to both application, deep application, and separation from the seed; or plough the soil early, thaw in the land Immediately after tilling, timely sowing to reduce root damage; or using biogas slurry to control root mites, in the early stage of root larvae damage, using the biogas slurry after fermentation to root, can kill roots and increase Organic fertilizer; or use grass ash to control root lice, plow a deep 5-10 cm ditch in the vegetable field with iron shovel, sprinkle grass ash in the ditch, cover the ditch and grass ash with soil, and then pour the water to the vegetable field. The fermented ash has good effect on controlling root lice.
2.2.8 Spodoptera litura can be controlled by reference to the control method of beet armyworm.
2.2.9 Cabbage worms can be controlled by reference to the control methods of beet armyworm.
2.2.10 The young larvae of the small ground tigers were diluted with 500-750 times with the nucleus of the nucleus and the genus Suspension sc (10 million PIB/mL of the genus Heliothis nucleopolyhedrovirus and 8 000 IU/L of Bacillus thuringiensis) Irrigation of vegetables with vegetables, every 7d1 times, continuous use 2 to 3 times; or control of small tigers with Beauveria bassiana, after 16:00 on cloudy or sunny days, 10 billion spores/g Beauveria bassiana 500-800 The diluted solution is sprayed, and sprayed continuously for 2 to 3 times every 7 days.
2.2.11 The yellow-curved beetle removes the yellow leaves of the vegetable field and removes the weeds so that it does not have wintering places and foodstuffs. Deep-cultivation of the soil before sowing, causing an environment that is not conducive to the life of the larvae and destroying some of the cockroaches. It is advisable to control the adult insects in the morning or evening, spraying 500-800 times dilution of 1% azadirachtin emulsifiable concentrate in the cotyledon stage, every 2 days, continuously spraying 2 to 3 times.
2.2.12 Radish borer (Rapeseed larvae) Controlled with Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt preparation), spray on the morning or evening larvae on sunny days, using 100 000 to 200 times diluted with 8 000 IU/μL Bt suspension for spray control. Spray every 2 to 3 times every 7d1 times, and pay attention to spraying the medicine into the heart of the radish.
2.2.13 Clean the idyllic locusts, remove weeds, fallen leaves, deteriorate the wintering conditions of adults, or pile up leaves and weeds in the field to lure or kill; or artificially kill, use the larvae to kill the mud, or to have mud or The wide-mouth container of the liquid medicine is taken under the leaves, shot down and concentrated to kill; or 10 to 100 million spores/g of Beauveria bassiana 300-500 times dilution, the surface of the soil is sprayed, and treated again 15 days later.
Biological pesticides are low-toxic and even non-toxic to humans and animals, and they are environmentally friendly and have been paid attention to by all parties. If you are not familiar with the technology of biopesticide use, you can refer to this article provided by Huinong.com!
Ungrouped,High Quality Ungrouped,Ungrouped Details, CN
Shenzhen Guangyang Zhongkang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.szlighttherapymachine.com
