Determination of Residual Organic Solvents in Amisulpride by Headspace Gas Chromatography
1 Introduction
The International Conference on Harmonizition (ICH) has a clear definition of drug residues and related guidelines. ICH classifies 69 organic solvents commonly used in the production and purification of pharmaceuticals into four categories according to the degree of harm to humans and the environment. The first type of solvent refers to a solvent which is known to be carcinogenic and is strongly suspected to be harmful to humans and the environment, and the residual amount thereof must be controlled within a prescribed range; the second type of solvent refers to a solvent which is non-genotoxic but has carcinogenicity to animals; Class 3 solvents refer to solvents that are less toxic to humans; Class 4 are solvents that do not have sufficient toxicological information (1-3). Amisulpride used organic solvents such as methanol and acetone in the extraction process. According to the above guidelines, methanol is the second type of solvent, and its content should not exceed 0.3%; acetone is the third type of solvent, and its content should not exceed 0.5%.
This paper describes the analytical method for the analysis of these two organic solvent residues in amisulpride using a Thermo Fisher gas chromatograph (with FID detector) and a Triplus headspace autosampler. The method validation shows that the method is accurate. effective.
2. Experimental methods
2.1 Instruments and reagents
Trace GC gas chromatograph (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with FID detector; column TR-V1 (30m x.25 mm x 3μm); Triplus HS autosampler (Thermo Mercury and acetone (chromatographically pure) were purchased from Sigma Co., Ltd.; N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF, analytical grade).
2.2 Chromatographic conditions
Temperature programming: initial temperature: 40 °C (60 min), heating rate: 30 °C/min to 200 °C (3 min)
Carrier gas: constant current mode, flow rate is 3ml/min
Inlet: 150 ° C, split injection, split ratio 10: 1
Detector temperature: 250 ° C
Headspace parameter settings:
Incubator temperature: 75 ° C
Incubation time: 30min
Injection volume: 1ml
3. Results and discussion
3.1 System adaptability
Since the residual solvent of the drug to be tested is mainly methanol and acetone, the above two organic solvents are selected and dissolved in DMF to examine the suitability of the system. A typical chromatogram is shown in Fig. 1. The results showed that the respective solvents were completely separated under the above chromatographic conditions.

figure 1
3.2 Headspace parameter optimization
3.2.1 Incubator temperature
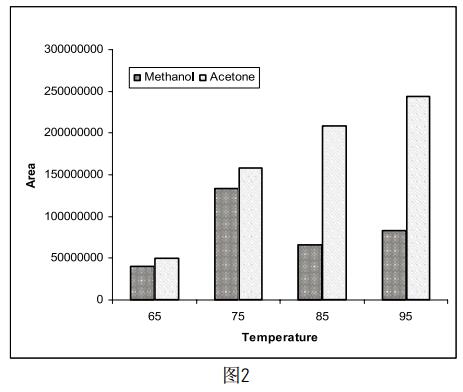
Take 5 mg of methanol and acetone, respectively, and dissolve in a certain amount of DMF so that the final volume of the solution is 5 ml. Four samples of the same concentration were prepared in parallel, and the temperature of the incubator was set to 65 ° C, 75 ° C, 85 ° C and 95 ° C, respectively, to determine the effect of different incubation times on the test results. The results (Figure 2) indicate that as the incubation temperature increases, the peak area of ​​acetone increases, but the response of methanol is highest at 75 °C, which is consistent with the recommended incubation temperature in the National Pharmacopoeia (75). °C~85°C). Moreover, since the chemical name of amoxicillin is 4-amino-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrole)methyl]-5-hexansulfonyl-2-methoxybenzamide, Huang Shizhen et al (4 Studies have shown that methoxy-containing samples degrade at higher headspace temperatures to produce methanol, and the rate of cracking is mainly affected by temperature. As the incubation temperature of the sample increases, the methanol content also increases significantly, thus affecting Real test results. So at the time of testing, we set the temperature of the incubator to 75 °C.
3.2.2 Incubation time
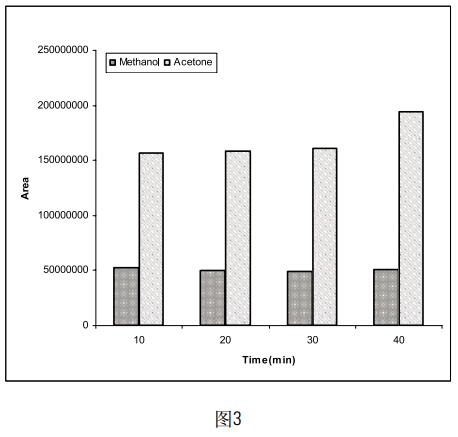
Take 5 mg of methanol and acetone, respectively, and dissolve in a certain amount of DMF so that the final volume of the solution is 5 ml. Four samples of the same concentration were prepared in parallel, and the temperature of the incubator was set to 10 min, 20 min, 30 min and 40 min, respectively, to determine the effect of different incubation times on the test results. The results (Figure 3) indicate that the peak areas of acetone and methanol do not change much with the increase of incubation time. Considering that the organic solvent in the sample may take a long time to facilitate its volatilization, we will hatch. The time is set to 20min.
3.3 standard curve, detection limit and precision
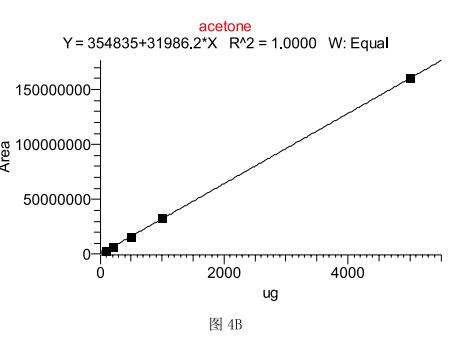
The method adopts the external standard method for quantification. Because of the headspace injection, considering the influence of different sample volumes on the gas expansion, the standard curve (5mg, the absolute weight of the corresponding component is taken as the peak area Y of the target component. 1mg, 500ug, 100ug and 50ug), Figures 4A and B show that both methanol and acetone have a very good linear relationship in this instrumental method. Taking 500ug as an example, the detection limit of methanol is 1.5ug according to the signal-to-noise ratio of 3, and the detection limit of acetone is 1ug. The methanol and acetone were set to 5 standards of 500 ug parallel. The reproducibility of the calculation method showed that the RSD value of methanol was 3.76%, and the RSD value of acetone was 1.39.

3.4 Sample testing
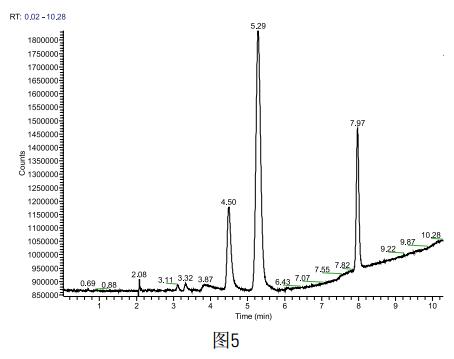
Weigh 1g sample accurately, dilute with a 10ml volumetric flask, take 5ml into the headspace bottle, and test the sample according to the above method. Each sample is inserted in parallel four times (the spectrum is shown in Figure 5). The results are shown in the following table. Show. According to the ICH standard, methanol is the second type of solvent, the content can not exceed 0.3%, acetone belongs to the third type of solvent, the content can not exceed 0.5%, the solvent residue in the sample to be tested is detected as methanol 0.004% and acetone 0.05% respectively. , in line with ICH standards.
3.5 Recovery experiment
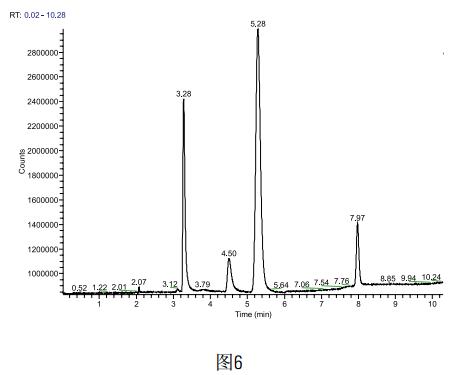
Weigh accurately 0.5g of the above sample powder, accurately add 500ug of methanol and acetone, and finally make up to 5ml with DMF, then carry out sample test, each sample is measured three times (sample is spiked as shown in Figure 6), and finally methanol and The average recovery of acetone was 98.4% and 101.7%, respectively.
3.6 Precautions
All sample dissolution and standard configuration procedures are performed on ice to prevent errors in the results caused by organic solvent evaporation.
references:
1. Zhou Haijun's main translation 1 International technical requirements for drug registration? Quality part [M] Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2000: 82
2. Chinese Pharmacopoeia [S]. Part II, 2000: Appendix 54
3. Residual Solvent Testing: A Review of Gas-Chromatographic and Alternative Techniques. Pharmaceutical Research, 2003, 20(3): 337-344
4. Determination of residual methanol in cefoxitin sodium by headspace capillary GC method. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceuticals 2007, 38(10): 727-728
The fish fat of mackerel has the functions of lowering blood fat, cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular diseases and prostate cancer. Eating more fish is good for health and can also supplement the lack of iron in the human body. For children and the elderly, mackerel It is the most suitable for them to eat and easy to supplement the required nutrients.
Horse Mackerel,Jack Mackerel,Fried Horse Mackerel,Deep-Fried Horse Mackerel
Zhejiang Industrial Group Co., Ltd. , https://www.xingyeseafood.com
