Paddle feeding
Paddlefish feed on zooplankton for life. Larval larvae are mainly small-branched broilers and also eat egg yolk, fish meal, and shrimp meal. Although the hatched larvae have some cracks, they cannot be closed, but only by constantly flowing to obtain oxygen and bait. The size of the bait should be compatible with its mouth cracks, such as rotifers. Only passive food intake, the order of requirements for feed: rotifers → small Cladocera → large Cladocera and copepods. Artificial feeding requires 9 to 10 feedings each time, feeding once every 2 hours, and feeding 3 to 5 grams of redworms or other small zooplankton per thousand fry. Only when the juveniles grow out of the snout can they have the initiative to ingest food. The feeding method is swallowing, and swallows zooplankton, small fish and shrimp. When the bait is insufficient, the larvae bite each other seriously, and it is necessary to increase the amount of bait feed and reduce the fry density. When the length of the carp seedlings exceeds 12 cm, the feeding organs develop well and they are transferred to filter-feeding methods. The buoyant food of zooplankton size is commonly eaten under captivity. Paddlefish are more mature than Chinese sturgeon and Daphnia magna. Male sexual maturity is usually 7-9 years, females are usually 8-10 years, and females are generally selected to produce about 18 kg. Female sex ratio is generally 1:1. Paddlefish broodstock has no obvious side sexual characteristics. In general, female individuals are large, abdominal distension, swollen, congested and slightly loosened near the urogenital port, and easy insertion of the urogenital port with little fingers; male individuals are smaller and have more protrusions on the head. A more reliable method is to observe the gonad with the naked eye. At present, the effect of oxytocin is better. The pituitary gland and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue (LRH-A) of the frozen paddlefish are common, and the pituitary gland of the paddlefish is commonly used. The females are generally used in two pituitary/tailed males and males in one pituitary/tail. After thawing the pituitary, 1.5 ml of deionized water was added, and after grinding, it was intraperitoneally injected. The injection method was one needle and the success rate was 65%. With LRH-A oxytocin has a good effect, the dose is generally 10mg per kilogram of body weight, more use of two-needle injection method, the gonads developed better broodstock, basically empty. After promoting estrus in the broodstock, eggs are collected, inseminated, de-adhered, and hatched to obtain fry. It should be noted that 24°C is the sublethal temperature for fry hatching and 28°C is the lethal temperature, while water temperature below 11°C will also reduce the survival rate and inhibit its growth. The optimum water temperature range is 20 to 24°C. In addition, larval rearing should be carried out indoors to avoid death caused by excessive temperature difference.
Halogen Operating Lamp With Camera System
Halogen Operating Lamp With Camera System. The built-in compact structure offers large scope of activity,flexible turning and stable performance, The use of effects is very good. Installation:the basement should support a burden of 500Kg;the lowest height for instal lation is 2.9m;If the height of the celling is more than 3.2m,one extension rack should be added(it can specially made by us). Micro-computer digital control has 8 shift scales and a good anti-jamming ability under AC180V-250V; Halogen Operating Lamp With Camera System with back up bulb automatic switch function ,auto-swift of backup bulb in 0.2 seconds faster than 0.5 seconds of other lamps will not effect the procedure of operation surgery;Soft boot device and an effective increase of bulb life-span.
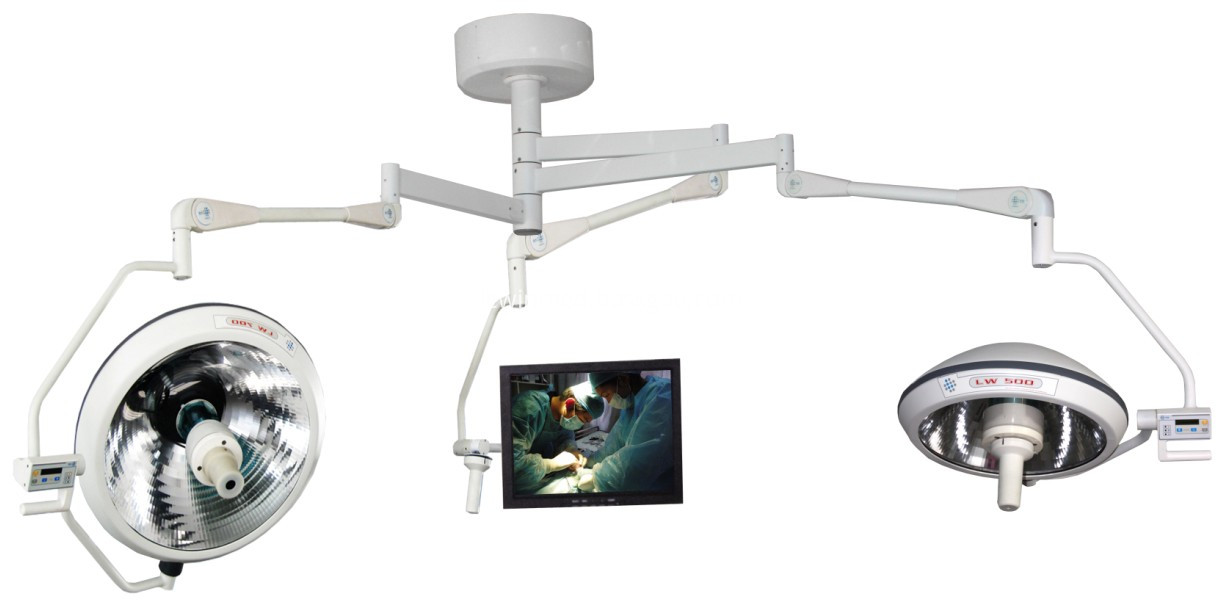
Camera Ceiling Operating Light,Camera Ceiling OT Light,Camera Operating Room Lamp,Camera Surgical Room Lamp
Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.operatinglight.nl
